Deep learning for reticular opacity on chest radiographs with interstitial lung disease

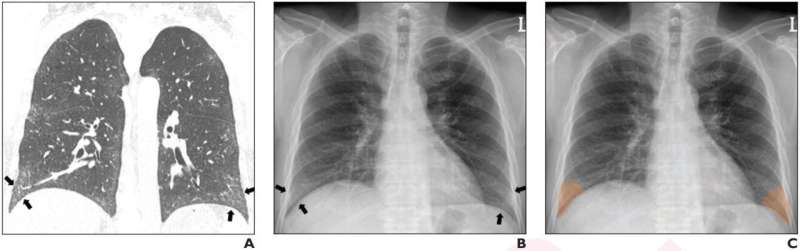
According to ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), radiologists’ sensitivity on chest radiographs for reticular opacity in patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD)—including those with mild disease—improved using a commercially available deep learning algorithm (DLA) from VUNO.
“Use of the DLA improved reader performance and interobserver agreement,” wrote corresponding author Sang Min Lee from Korea’s Asan Medical Center in Seoul, noting that the “benefits were more notable in terms of sensitivity than specificity.”
Lee and team’s retrospective study included 197 patients (130 men, 67 women; mean age, 62.6 years) with surgically proven ILD between January 2017 and December 2018 who underwent preoperative chest radiography and chest CT within a 30-day period. The VUNO Med–Chest X-ray DLA was used to detect lower lobe or subpleural abnormalities; those matching reticular opacity location on CT were deemed true-positives. Six readers (three thoracic radiologists and three residents) independently reviewed radiographs for reticular opacity presence with and without DLA.
In samples from two centers, the VUNO DLA’s accuracy for reticular opacity detection on chest radiograph was 98.5% and 100.0%. Additionally, the DLA improved reader sensitivity from 66.7% to 86.8% in mild, 84.2% to 99.8% in moderate, and 87.3% to 100.0% in severe disease. The DLA also improved interobserver agreement from kappa of 0.517 to 0.870.
Source: Read Full Article




